Presentation Transcript
Slide 1: Introduction
Slide 2: Obsolete and Emerging Technology
Dr. Thornburg (2009) states that an emerging technology means different things to different people because it depends on the technological use of the tool in everyday practice. Therefore, the term “emerging” is relative to each community where the tool is being used. For this presentation, I will evaluate an obsolete and an emerging technology used in the workplace; concentrating on the storage and transfer of data.
Historically humans attempted to discover a better way to store data from storing scrolls in pottery, to current emerging technology where it is stored via cloud computing.
Slide 3: Data storage
In the last few years, the idea of cloud computing has taken over individuals and organizations.The way we save and backup our files are changing, which is opening new doors to collaboration among professionals, students, and organizations. Our storage media has evolved from floppy disks, CDs, flash drives, external hard drives and other storage devices.
With the cloud, there is no need to carry all of the files and there is no threat of the loss of a storage media, which translates into lost work. Now, it all “sits” on a cloud in a centralized location, which can easily be retrieved with an Internet connection.
Even though some types of cloud computing are free or less expensive infrastructure operations and maintenance environment options for educational organizations, it is not yet a commonly supported tool and it is still considered an emerging technology by some.
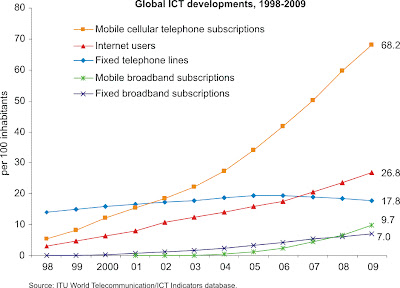
Slide 4: Data storage historical overview
Slide 5 What is Cloud Computing?
It consists of the delivery of application, infrastructure, and storage over the Internet based on client demand.
A cloud computing network can contain public, private, or hybrid clouds (a combination of both public and private).
Cloud computing can remove many of the limitations found in a conventional computing environment, such as: space, time, power, and cost.
Slide 6 : Cloud Computing
Cloud computing not only changes how we store and retrieve applications and files, but also how we communicate and share them with other members of our group, and how organizations restructure and modernize their IT infrastructure.
An example is Dropbox.com, a free website where users can save files on the cloud, and which also allows users to share particular files with others and to retrieve them from any mobile device.
Slide 7: DropBox.com
Slide 8: McLuhan's Laws of Media
By looking at tetrads, we can see that there is a connection between obsolete and emerging technology as the tool is in constant progression.
Dr. Thornburg (2008) states: “The ‘new’ drives an older technology into obsolescence” (p.2); meaning that every emerging idea is constructed on a previous one. The retrieval part of the tetrad is an example of how even ancient tools set the stage for current technological ideas.
Each emerging technological advance is also dependent on additional factors and technological advances
Slide 9: McLuhan’s Tetrad
McLuhan’s tetrad forces you to think about artifacts in a new way making you more aware of new technologies as they emerge” (Thornburg 2009).
Technology planning is an important factor for any IT personnel in any organization. McLuhan Tetrad is helpful with regards to looking at emerging and emerged technology from different perspectives, and asking questions such as is this technology beneficial to learners and how can it evolve.
- McLuhan's tetrad asks four questions that determine the technologies affect on the workplace and society. The four questions are:
- What does this technology enhance?
- What does it obsolete?
- What does it retrieve?
- What does it reverse?
Slide 11: Emerged Technology Tetrad
Slide 12: Interview with IT Specialists and
Decision-Maker Mr. Asif Hussain, Kingsborough’s Chief Information Officer (CIO) Mr. Hussain has incorporated many technological changes and improvements at Kingsborough Community College, Brooklyn, NY. One of his initiatives was the integration of cloud computing
Slide 13: Interview Transcript with Mr. Hussain
Slide 14: Video Interview with Mr. Hussain
Slide 15: Interview with IT Specialist Mr. Kwatei Jones-Quartey, Kingsborough’s Senior Web Programmer
Slide 16: Video Interview with Mr. Kwatei Jones-Quartey
Slide 17 : Interview Transcript with Mr. Kwatei Jones-Quartey
Interview Questions for IT Specialist Mr. Kwatei Jones-Quartey
- How many years have you been working at Kingsborough Community College?
- Are you a decision-maker, a user of the technology, or both in your department?
- What technological changes have you seen in your workplace with regards to how you store and transfer data?
- Have these transformations affected your work?
- Do you think it makes your work more efficient?
Slide 19: Consent form
Slide 20: Six Forces That Drive Emerging Technology
- Evolutionary Technology (based on Moore’s Law)
New ideas based on developed technology. - Rhymes of History
New technology which has emerged due to the impact felt many years before from another technology, or when a technology rekindles something from the past. - Disruptive Technology
One that does not create a new market, but changes the product.
A new technology that disrupts existing technology and pushes it out - Science Fiction
Creative forces that expand and generate new creative technological ideas - Increasing Returns
One technology’s ability to capitalize on the popularity of other technological advances to rise and become popular. - Red Queens
Two technologies competing for the same market share where, in the process, all other competitors are left behind (Thornburg, 2008d, p.12).
Moore law- Trends in technologies in which the power of technology doubles about every 12 months.
Moore’s laws are even more emphasized in current rapid technological evolvements. Not only are technological tools becoming more powerful and less expensive, but some are even free due to the cloud computing and just as powerful.
The key principle of evolutionary technology is that technology is changing according to the social needs of society.
The current social technological need is for technology to be easily transported, less expensive, and more efficient. Therefore, it is possible to predict future trends if we look at societal evolution.
Slide 22: Six Forces That Drive Emerging Evolutionary Technology Continue
The Internet was mainly developed by scientists because there was a need to share data with other scientists that were remotely located. Although researchers could use the ARPANET from 1969, it only became available to the public in 1991, which was one of the reasons for its rapid growth and development; it also opened doors to closed societies.
This also led to the expansion of other technologies, which rely on the Internet and which has affected how we connect, communicate, save, and transfer data; it has even changed how we teach and learn.
Social entrepreneurs are looking at social needs and of already existing tools. This allows this technology to continuously evolve.
Slide 23 : Six Forces: Evolutionary Technologies on Obsolete Data Storage and Transfer Technology
The evolutionary path where new technological ideas are a progression or a growth of previous ones (Thornburg, 2009).
External drives became obsolete because there is no need to back up files on drives with limited storage capacity and it eliminated the need to carry the drive with you.
Cloud computing allows for high capacity file storage, file sharing, and access from any device connected to the Internet.
Slide 24: Six Forces: Evolutionary Technologies on Emerging Cloud Computing Storage Technology Dropbox.com
Dropbox.com is a Web-based file hosting service operated by Dropbox.com Inc. that uses cloud computing to enable users to store and share files for free (there are some paid services, with varying options). The files can be retrieved from any location with an Internet connection, and it also uses mobile technology.
Slide 25: Six Forces: Rhymes of History on Obsolete Data Storage and Transfer Technology
Dr. Thornburg similarly describes one of the forces that drives emerging technology as “Rhymes of History.” This term is used to define a new technology which has emerged due to the impact felt many years before from another technology, or when a technology rekindles something from the past.
We use the cloud computing to store, retrieve, and transmit data, in addition to communicating; and new technologies are continuously emerging.
Slide 26 : Six Forces: Rhymes of History on Obsolete Data Storage and Transfer Technology and Original Emerge
Rhymes of history have been continuously rekindled. Evidenced from the progression from oral communications, to storing data in pottery, to an external floppy disks, external drives and USB flash drives, to cloud computing communication and data transfer information.
These are new ideas of how to save and communicate information which are built on old ideas: the need of portably storing information with easy transfer and retrieval.
Slide 27 : Six Forces: Rhymes of History on Obsolete Data Storage and Transfer Technology and Original Emerge
- Limited storage space of external hard drives and the cost of maintenance of on-campus servers has created limitations.
- The expansion of the Internet and the availability of cloud computing has opened up new opportunities for students, faculty, and staff to save their data and make it available to other.
- Learners now have the opportunity to have an open communicational channel with their educators.
- The rhymes of history have rekindled oral communication to current oral communications on Skype.
- From saving data using pottery, to current emerging technology where it is stored via cloud computing.
Learners have constant access to information and educational material, and they can access applications from home.
This is unlike traditional access to data, which could only be done physically on campus.
Slide 29: Six Forces: Disruptive technology on Obsolete Technology’s Original Emerge
Dr. Thornberg (n.d.) states that technologies sprout quickly and disrupt existing technologies.
Christensen (2002) breaks down disruptive technology into two types: One that does not create a new market, but changes the product, and the other is a new technology that disrupts existing technology and pushes it out.
Slide 30: Six Forces: Disruptive technology on Obsolete Technology
Portable external drives were a disruptive technology because it was a new way to store files when compared to internal computer hard drives.
Slide 31: Six Forces: Disruptive Technology on Emerging Technology
A new technology with the same functionality of an existing technology, but which functions more efficiently is a disruptive technology.
As bandwidth becomes more available, more applications are emerging. Companies using cloud computing are offering free storage space to individuals.
Users can share cloud server space cooperatively, purchase applications, and share open and closed networks.
Slide 32: Six Forces: Science Fiction on Obsolete Technology’s Original Emergence
Science fiction technology, according to Thornburg (2009b), can prompt ideas that motivate inventors to make fictional technology reality.
Slide 33: Six Forces: Science Fiction on Obsolete Technology
Portable data storage and cloud computing has its beginnings in science fiction books and movies as virtual cyberspace.
An example is The Minority Report movie, Isaac Asimov and the Foundation series, and William Gibson short story, Burning Chrome.
Slide 34: Six Forces: Science Fiction on Emerging Technology
The storage of data is taken into cyberspace, where science fiction and reality becomes distorted as people connect, save, and manage data on a “cloud.”
Slide 35: Six Forces: Increasing Returns on Obsolete Technology’s Original Emergence
Thornburg(2009) defines “Increasing Returns” as two technologies competing for the same market share. One of these technologies is adapted and seizes the market, even when the other has better technology (p.12).
Slide 36: Six Forces: Increasing Returns on Obsolete Technology
Companies such as Google and Microsoft Windows Live compete for space on the cloud.
Free options are taking over as options for personal users become available such as Dropbox.com which is used for data storage and makes obsolete the use of external drives and the need to carry them around.
Slide 37: Six Forces: Increasing Returns on Emerging Technology
There continues to be competition as to who will dominate cloud computing.
Google and Microsoft are using two different technologies. There is no need to download and install Google, unlike Microsoft ‘s products. Google is using “pure” clouding computing, where all of the documents and applications are only on the cloud; whereas Microsoft still uses traditional desktop applications in order to create and manage the data.
Microsoft has signed a long contract with CUNY colleges (25 colleges) and continues to dominate in its existing market share.
Slide 38: Six Forces: Increasing Returns on Emerging Technology
Image of Window Life and DropBox.com
Slide 39: Six Forces: Red Queens on Obsolete Technology’s Original Emergence
Thornburg(2008) defines a Red Queen as two technologies competing for the same market share (p.12).
Slide 40: Six Forces: Red Queens on Obsolete Technology
The Upstartle Company used “Writely” (Web-based word processor, spreadsheet, presentation, form, and data storage service ) and was one of the first companies to have users use it’s web-based word processors and save the files on its servers.
However, Google, by building upon Writely’s idea and incorporating its own already developed product of Google Spreadsheets, created Google Doc. In 2006, Google bought Upstartle (http://www.cbronline.com/blogs/technology/writely_or_wron).
Slide 41: Six Forces: Red Queens on Emerging Technology
Chris Anderson (2004) notes that new technologies were able to capitalize on the popularity of other technological advances to rise and become popular.
By offering free online services for storing, sharing, and creating documents, Google has also become a Red Queen for Microsoft who dominated the market for doc. software which is installed on computer hard drives.
Slide 42: Future of Cloud Computing
The file sharing and synchronization service provider Dropbox announced on Jan 20, 2010 that it has passed the 4,000,000 user milestone.
Dropbox was founded in 2007.
http://techcrunch.com/2010/01/20/dropbox-4-million-user/.
While Dropbox functions as a storage service, it focuses on synchronization and sharing. Dropbox uses Amazon's S3 storage system to store the files. To succeed and grow in the market, companies will continue to share resources and marketing in order to stay ahead of other competitors.
Slide 43: Future of Cloud Computing
As more companies begin to offer services on the cloud, the cloud’s applications and services will continue to grow and improve. Businesses and private users will reduce and eliminate the need to purchase and maintain software's and hardware. Furthermore, more real time communication and collaboration would be available 24/7 .
According to the research by the Pew Research Center, by 2020, most people will access software applications online and share and access information through the use of remote server networks, rather than depending primarily on tools and information housed on their individual, personal computers (http://pewresearch.org/pubs/1623/future-cloud-computing-technology).
Slide 44: Reference
Anderson, C. (2004). Tech’s long tail [Video]. Retrieved from http://www.ted.com/index.php/talks/chris_anderson_of_wired_on_tech_s_long_tail.html
Christensen, C. (2002). The innovation economy: How technology is transforming existing industries and creating new ones [Video]. Retrieved from h t t p : / / pewresearch.org/pubs/1623/futurecloud-computing-technology-experts
Friedman, N. (2009). The high cost of computers? U.S. Naval Institute Proceedings, 135(3), 90−91.
Kelly, K. (2007, December). The next 5,000 days of the web [speech]. Speech delivered at the EG 2007 Conference, Los Angeles. Retrieved from http://www.ted.com/index.php/talks/kevin_kelly_on_the_next_5_000_days_of_the_web.html
Linden Labs http://wiki.secondlife.com/wiki/Second_Life_Education
Pew Internet & American Life Project. (2010, June 11). The future of cloud computing. Retrieved from http://pewresearch.org/pubs/1623/future-cloud-computing-technology-experts
Soloway, E. (Producer). (nd). Emerging vs. emerged technologies [Audio Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Soloway, E. (Producer). (nd). Resilience and Risk Taking in Educational Technology [Audio Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Slide 45: Reference Continue
Thornburg, D. (2008). Red Queens, butterflies, and strange attractors: Imperfect lenses into emergent technologies. Lake Barrington, IL: Thornburg Center for Space Exploration.
Thornburg, D. D. (2008a). Emerging technologies and McLuhan's Laws of Media. Lake
Thornburg, D. (2008b). An amazingly incomplete emerging technologies bibliography. Lake Barrington, IL: Thornburg Center for Space Exploration.
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). Evolutionary Technologies. [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). Six forces that drive emerging technology. [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Thornburg, D. (2009). When is a Technology Emergent?. Retrieved from http://sylvan.live.ecollege.com/ec/courses/14936/CRS-WUEDUC8812-3730077/when_is_a_technology_emergent.pdf
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). McLuhan Tetrad. [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). Rhymes of history. [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). Six forces that drive emerging technology. [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). What is emerging technology? [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.
Thornburg, D. (Producer). (nd). Disruptive Technology. [Video Podcast]. Laureate Education, Inc.